40 indexing using labels in dataframe
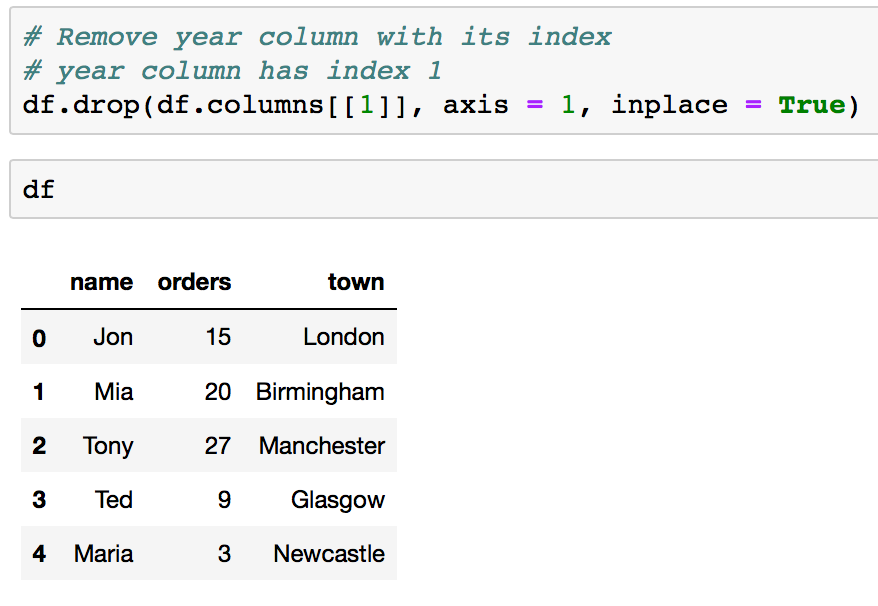
How to drop rows in DataFrame by index labels - BTech Geeks For this we are going to use the drop ( ) function. Syntax - DataFrame.drop ( labels=None, axis=0, index=None, columns=None, level=None, inplace=False, errors='raise' ) Where, the function accepts name/series of names in the label and deletes the rows or columns it points to. The axis is used to alter between rows and columns, 0 means rows and ... Boolean Indexing in Pandas - GeeksforGeeks In boolean indexing, we will select subsets of data based on the actual values of the data in the DataFrame and not on their row/column labels or integer locations. In boolean indexing, we use a boolean vector to filter the data. Boolean indexing is a type of indexing that uses actual values of the data in the DataFrame.
dynamic indexing using labels in pandas - Stack Overflow I would like to dynamically index elements of a pandas DataFrame using labels. Say I have df1 = pd.DataFrame (np.random.randn (6, 4), index=list ('abcdef'), columns=list ('ABCD')) and I want the element with labels 'a' and 'A'. "Statically" it's easy: df1.loc ['a','A'] But how to do build such a query dynamically at runtime?

Indexing using labels in dataframe
Pandas Select Rows by Index (Position/Label) In this article, I will explain how to select rows from pandas DataFrame by integer index and label, by the range, and selecting first and last n rows with several examples. loc [] & iloc [] operators are also used to select columns from pandas DataFrame and refer to related article how to get cell value from pandas DataFrame. How to Get the Index of a Dataframe in Python Pandas? Method 1: Using for loop. In Python, we can easily get the index or rows of a pandas DataFrame object using a for loop. In this method, we will create a pandas DataFrame object from a Python dictionary using the pd.DataFrame () function of pandas module in Python. Then we will run a for loop over the pandas DataFrame index object to print the ... How to Select Rows by Index in a Pandas DataFrame - Statology .iloc selects rows based on an integer index. So, if you want to select the 5th row in a DataFrame, you would use df.iloc [ [4]] since the first row is at index 0, the second row is at index 1, and so on. .loc selects rows based on a labeled index. So, if you want to select the row with an index label of 5, you would directly use df.loc [ [5]].
Indexing using labels in dataframe. pandas: Rename columns/index names (labels) of DataFrame Specify new column/index names as the first parameter labels in a list-like object such as list or tuple. Setting the parameter axis to 0 or 'index' updates index, and setting it to 1 or columns updates columns. If omitted, index will be updated. Indexing and Sorting a dataframe using iloc and loc Labels based indexing using loc. To index a dataframe based on column names, loc can be used. For example, to get all the columns between petal_length till iris class and records from 2nd to 10th, can be extracted by using - ... Simples way to sort a dataframe can be done using sort_values function of pandas dataframe, which take the column ... How to get the names (titles or labels) of a pandas data frame in python To get the names of the data frame rows: >>> df.index Index(['Alice', 'Bob', 'Emma'], dtype='object') Get the row names of a pandas data frame (Exemple 2) Another example using the csv file train.csv (that can be downloaded on kaggle): >>> import pandas as pd >>> df = pd.read_csv('train.csv') >>> df.index RangeIndex(start=0, stop=1460, step=1) Working With Specific Values In Pandas DataFrame - Data Courses This function of a pandas DataFrame is of high value as you can build an index using a specific column, (meaning: a label) that you want to use for managing and querying your data. For example, one can develop an index from a column of values and then use the attribute.loc to select data from pandas DataFrame based on a value found in the index.
Tutorial: How to Index DataFrames in Pandas - Dataquest Let's explore four methods of label-based dataframe indexing: using the indexing operator [], attribute operator ., loc indexer, and at indexer. Using the Indexing Operator If we need to select all data from one or multiple columns of a pandas dataframe, we can simply use the indexing operator []. Indexing, Slicing and Subsetting DataFrames in Python Describe what 0-based indexing is. Manipulate and extract data using column headings and index locations. Employ slicing to select sets of data from a DataFrame. Employ label and integer-based indexing to select ranges of data in a dataframe. Reassign values within subsets of a DataFrame. Create a copy of a DataFrame. Indexing a Pandas DataFrame for people who don't like to remember things In pandas data frames, each row also has a name. By default, this label is just the row number. However, you can set one of your columns to be the index of your DataFrame, which means that its values will be used as row labels. We set the column 'name' as our index. It is a common operation to pick out one of the DataFrame's columns to work on. pandas.DataFrame.set_index — pandas 1.4.2 documentation DataFrame.set_index(keys, drop=True, append=False, inplace=False, verify_integrity=False) [source] ¶ Set the DataFrame index using existing columns. Set the DataFrame index (row labels) using one or more existing columns or arrays (of the correct length). The index can replace the existing index or expand on it. Parameters
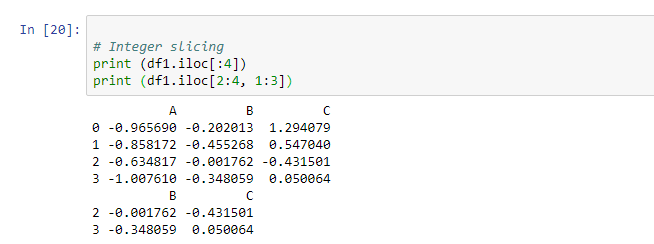
How to Index Data in Pandas with Python - Medium Using Single Label. One way we can specify which rows and/or columns we want is by using labels. For rows, the label is the index value of that row, and for columns, the column name is the label. For example, in our ufo dataframe, if we want the fifth row only along with all the columns, we would use the following: ufo.loc [4, :] Indexing and selecting data — pandas 1.4.2 documentation pandas provides a suite of methods in order to have purely label based indexing. This is a strict inclusion based protocol. Every label asked for must be in the index, or a KeyError will be raised. When slicing, both the start bound AND the stop bound are included, if present in the index. How to select subset of data with Index Labels in Python Pandas? With.iloc attribute,pandas select only by position and work similarly to Python lists. The .loc attribute selects only by index label, which is similarto how Python dictionaries work. Select a Subset Of Data Using Index Labels with .loc[] The loc and iloc attributes are available on both Series and DataFrame Pandas DataFrame Indexing - KDnuggets In pandas data frames, each row also has a name. By default, this label is just the row number. However, you can set one of your columns to be the index of your DataFrame, which means that its values will be used as row labels. We set the column 'name' as our index. It is a common operation to pick out one of the DataFrame's columns to work on.
Set Index in pandas DataFrame - PYnative We need to pass the column or list of column labels as input to the DataFrame.set_index () function to set it as an index of DataFrame. By default, these new index columns are deleted from the DataFrame. df = df.set_index ( ['col_label1', 'col_label2'…]) Set the index in place. We can use the parameter inplace to set the index in the existing ...
Pandas: Create an index labels by using 64-bit integers, floating-point ... Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus. Previous: Write a Pandas program to display the default index and set a column as an Index in a given dataframe and then reset the index. Next: Write a Pandas program to create a DataFrame using intervals as an index.
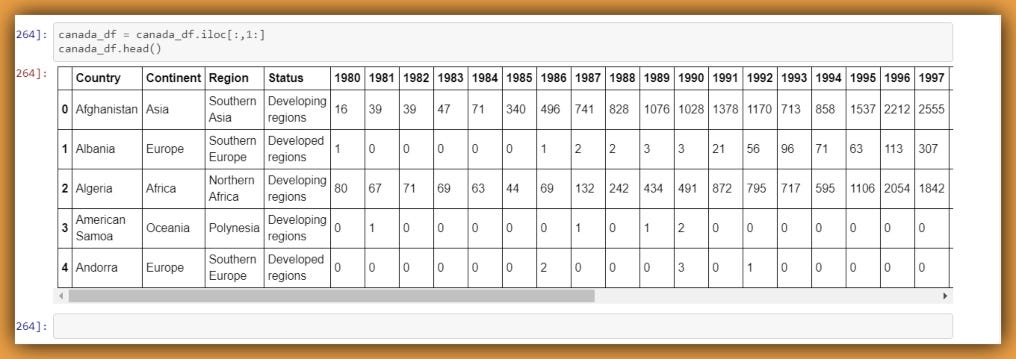
How to Filter a Pandas DataFrame With a Multi-Level Column Index ... The dataframe where data under the "AAPL" column label in the "Close" column is greater than 100. Notice that we used a "." to navigate the first column label.
How to Select Columns by Index in a Pandas DataFrame If you'd like to select columns based on label indexing, you can use the .loc function. This tutorial provides an example of how to use each of these functions in practice. Example 1: Select Columns Based on Integer Indexing
Indexing in Pandas Dataframe using Python - Medium Indexing using .loc method. If we use the .loc method, we have to pass the data using its Label name. Single Row To display a single row from the dataframe, we will mention the row's index name in the .loc method. The whole row information will display like this, Single Row information Multiple Rows
Python Pandas: Get Index Label for a Value in a DataFrame If I know the value in 'hair' is 'blonde', how do I get the index label (not integer location) corresponding to df.ix['mary','hair']? (In other words, I want to get 'mary' knowing that hair is 'blonde'). If I wanted the integer value of the index I'd use get_loc. But I want the label. Thanks in advance.
Pandas DataFrame Indexing: Set the Index of a Pandas Dataframe Python list as the index of the DataFrame In this method, we can set the index of the Pandas DataFrame object using the pd.Index (), range (), and set_index () function. First, we will create a Python sequence of numbers using the range () function then pass it to the pd.Index () function which returns the DataFrame index object.
Pandas Set Column as Index in DataFrame - Spark by {Examples} Use DataFrame.set_index () method to set the existing column of DataFrame as an index. On DataFrame, the row label is an Index. If your DataFrame has already had an Index, this replaces the existing index or expands on it. You can set the DataFrame index (row labels) using one or more existing columns or arrays (of the correct length). Syntax:
How to find index of value in Pandas dataframe - DevEnum.com 2. df.index.values to Find index of specific Value. To find the indexes of the specific value that match the given condition in Pandas dataframe we will use df ['Subject'] to match the given values and index. values to find an index of matched value. The result shows us that rows 0,1,2 have the value 'Math' in the Subject column.
Label-based indexing to the Pandas DataFrame - GeeksforGeeks In the above example, we use the concept of label based Fancy Indexing to access multiple elements of data frame at once and hence create two new columns ' Age ' and ' Marks ' using function dataframe.lookup () Example 3: Python3 import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame ( [ ['Date1', 1850, 1992,'Avi', 5, 41, 70, 'Avi'],
How to Select Rows by Index in a Pandas DataFrame - Statology .iloc selects rows based on an integer index. So, if you want to select the 5th row in a DataFrame, you would use df.iloc [ [4]] since the first row is at index 0, the second row is at index 1, and so on. .loc selects rows based on a labeled index. So, if you want to select the row with an index label of 5, you would directly use df.loc [ [5]].
How to Get the Index of a Dataframe in Python Pandas? Method 1: Using for loop. In Python, we can easily get the index or rows of a pandas DataFrame object using a for loop. In this method, we will create a pandas DataFrame object from a Python dictionary using the pd.DataFrame () function of pandas module in Python. Then we will run a for loop over the pandas DataFrame index object to print the ...
Pandas Select Rows by Index (Position/Label) In this article, I will explain how to select rows from pandas DataFrame by integer index and label, by the range, and selecting first and last n rows with several examples. loc [] & iloc [] operators are also used to select columns from pandas DataFrame and refer to related article how to get cell value from pandas DataFrame.









Post a Comment for "40 indexing using labels in dataframe"